Research Experience
1. Multi-Modal Transformer Framework for Metal-Organic Framework Property Prediction
2024.01 - 2024.11
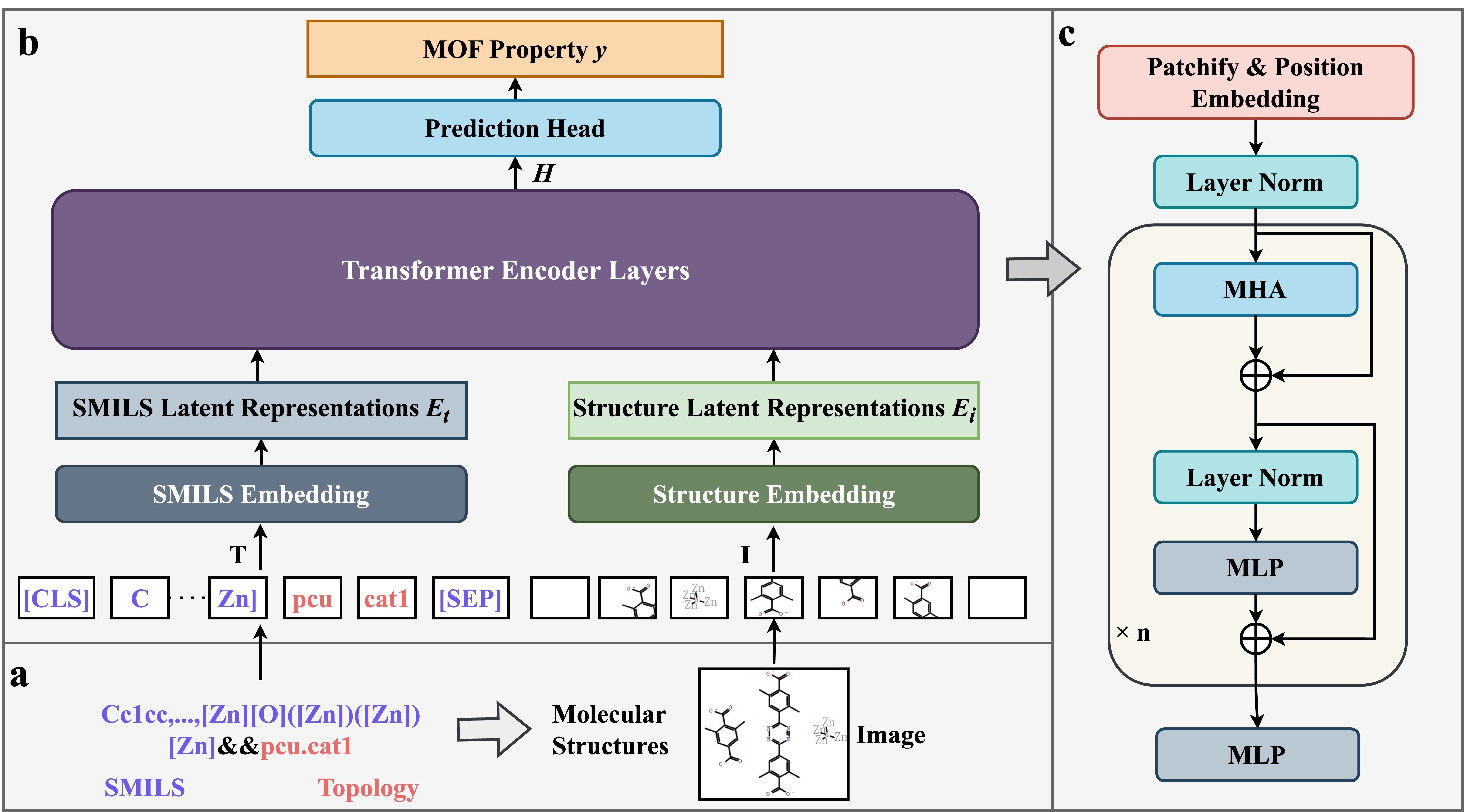
Figure 1: The schematic diagram of the proposed M-MOFormer.
- Developed M-MOFormer, a novel multi-modal transformer framework that integrates SMILES representations and automatically generated 2D structural diagrams through a self-developed openchemlib-MMOF package, significantly advancing the field of structure-agnostic MOF property prediction.
- Designed and implemented a dual-pathway transformer architecture featuring cross-modal attention mechanisms to effectively combine structural information from both textual and visual modalities, achieving superior prediction accuracy compared to existing structure-agnostic approaches while maintaining computational efficiency.
- Open-sourced a comprehensive multi-modal MOF prediction dataset and validated the framework's effectiveness through extensive experiments on two public datasets (QMOF and hMOF), demonstrating 7-11% improved prediction accuracy over state-of-the-art baselines while providing interpretable insights into structure-property relationships.
2. Synthesis of Multielemental Transition Metal Chalcogenides for Electrocatalytic Water Splitting
2021.04 - 2022.06
2.1 Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Performance of Ternary Transition Metal Sulfide NiFeV-S/NF
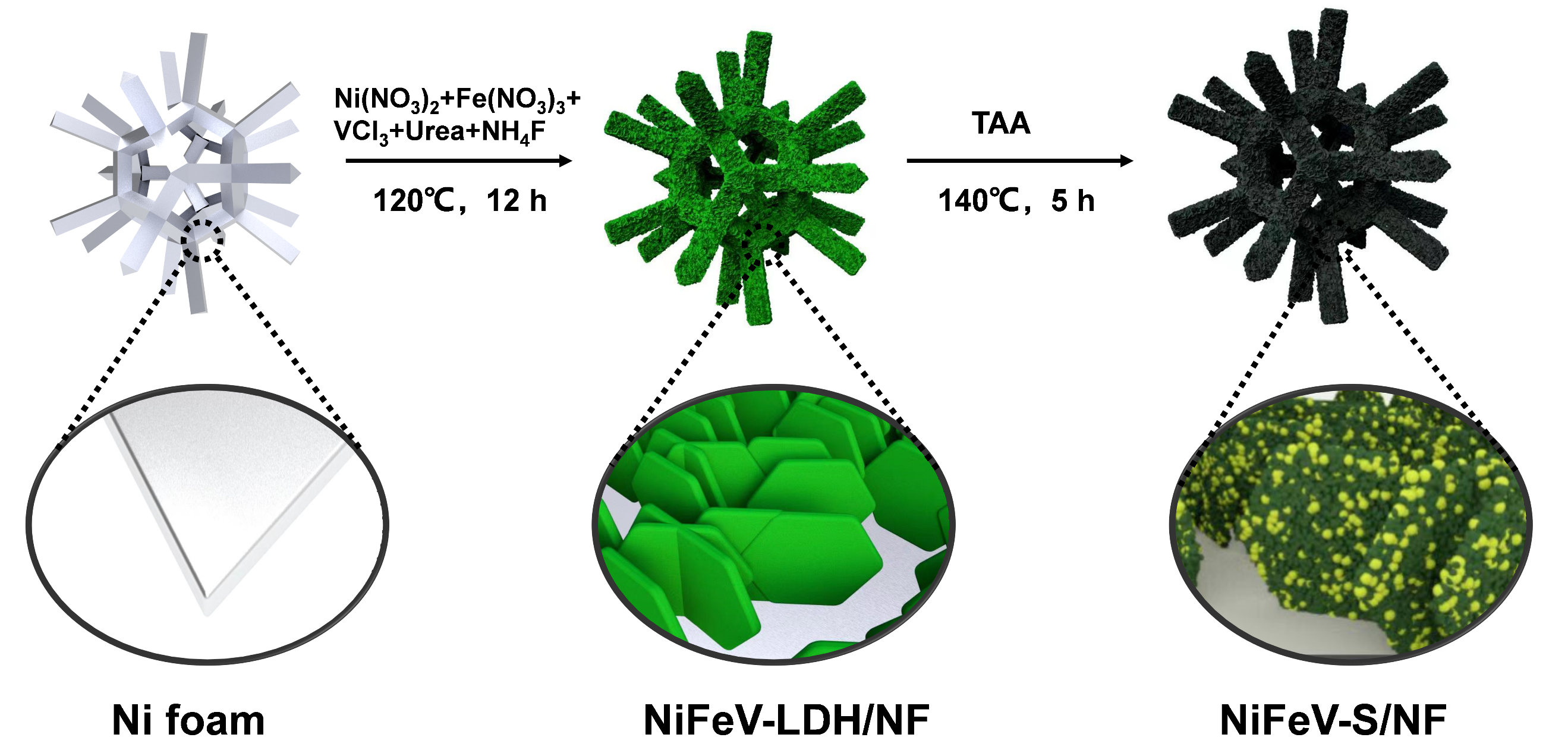
Figure 2: Schematic illustration of the synthesis of ternary metal sulfide NiFeV-S/NF.
- Developed a ternary transition metal sulfide NiFeV-S/NF catalyst via a two-step hydrothermal synthesis method to address the limitations of NiFe-LDH catalysts.
- Demonstrated superior electrocatalytic activity with overpotentials of 211 mV and 127 mV for OER and HER respectively, at a current density of 10 mA cm-2 in 1 M KOH.
- Fabricated a NiFeV-S/NF//NiFeV-S/NF electrolyzer for overall water splitting, demonstrating outstanding performance with a low cell voltage of 1.573 V at 10 mA cm-2.
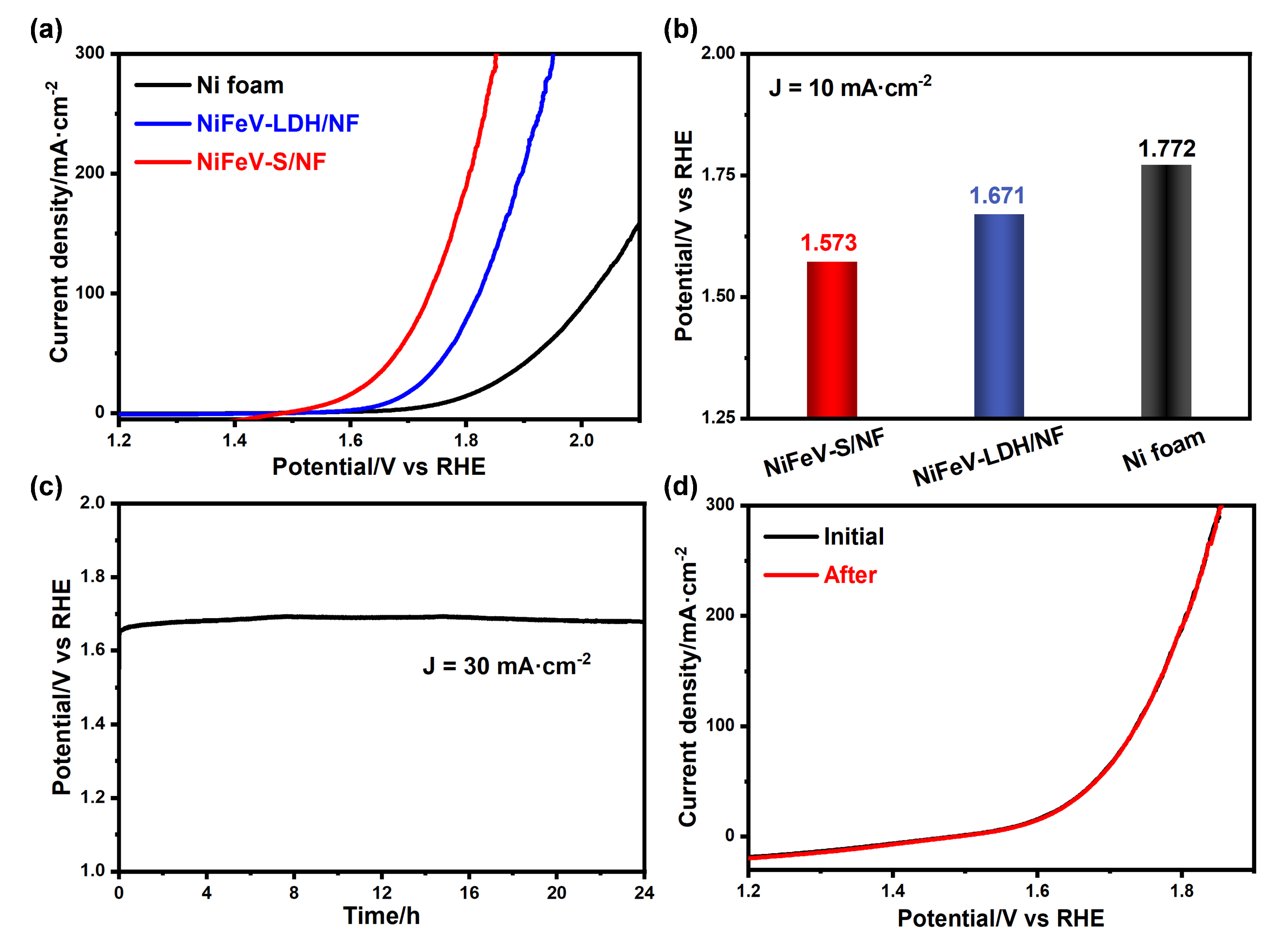
Figure 3: (a) Overall water splitting performance curves of Ni foam, NiFeV-LDH/NF, and NiFeV-S/NF; (b) Comparison of overall water splitting performance at 10 mA·cm-2; (c) Stability test curve of NiFeV-S/NF for overall water splitting; (d) Overall water splitting performance curves of NiFeV-S/NF before and after stability test.
2.2 Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Performance of NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF Heterojunction Catalyst
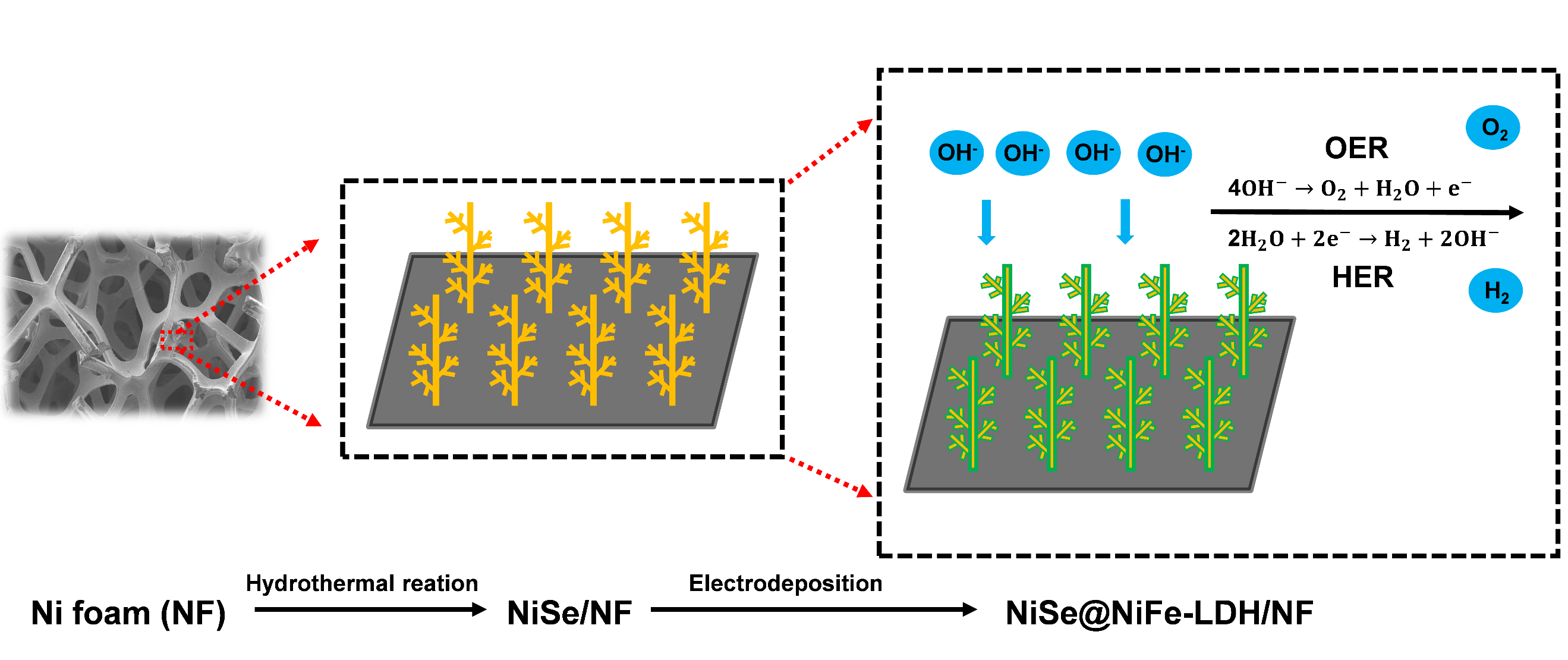
Figure 4: Schematic illustration of the synthesis of NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF heterojunction catalyst.
- Conceptualized and fabricated a novel core-shell heterostructured bifunctional electrocatalyst (NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF), combining the high conductivity of NiSe with the catalytic activity of NiFe-LDH.
- Achieved exceptional electrocatalytic activity in alkaline conditions, used as both cathode and anode for electrocatalytic water splitting requiring only 1.560 V to deliver a current density of 10 mA cm-2, surpassing the performance of previous catalysts.
- Conducted long-term stability tests to verify the durability enhancements provided by the core-shell architecture, contributing to the design of efficient and stable non-noble metal bifunctional catalysts.
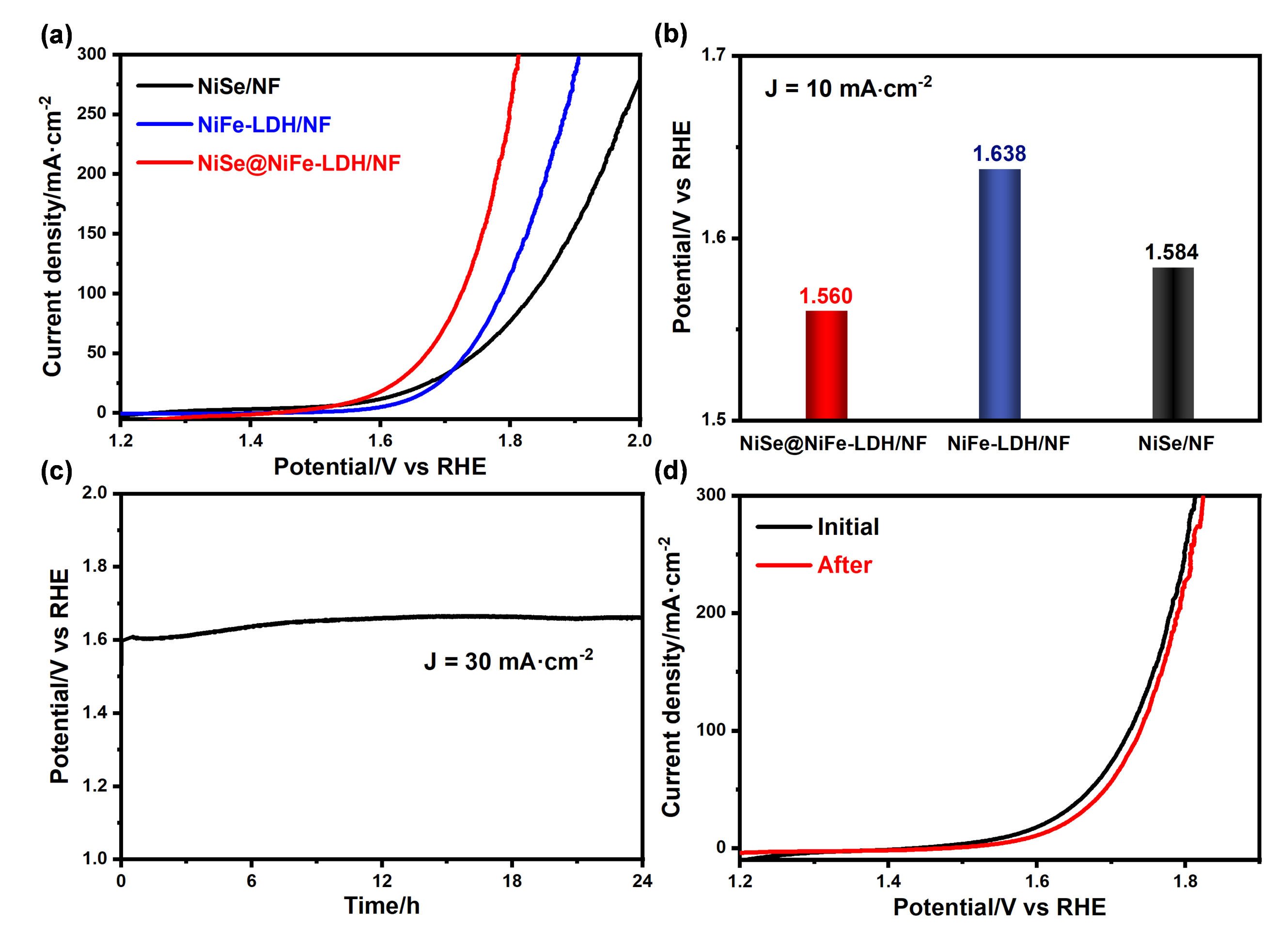
Figure 5: (a) Overall water splitting performance curves of NiSe/NF, NiFe-LDH/NF, and NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF; (b) Comparison of overall water splitting performance of catalysts; (c) Stability test curve of NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF for overall water splitting; (d) Overall water splitting performance curves of NiSe@NiFe-LDH/NF before and after stability test.
3. Synthesis of Pd@Ir and Investigation of Ir Facet Effects on OER Activity
2020.05 - 2021.06
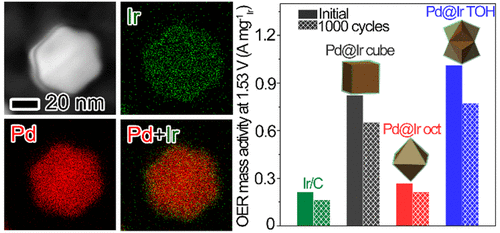
Figure 6: Preparation of Pd@Ir and study of the influence of different Ir crystal facets on OER activity.
- Developed a facile seed-mediated growth method to synthesize Pd@Ir core-shell nanocatalysts with controlled morphologies, employing facet-specific inhibitors and reaction kinetics control to tune the surface structure.
- Systematically investigated the structure-activity relationship of Ir-based catalysts by fabricating three Pd@Ir nanostructures with identical size but distinct surface facets, addressing the scalability limitations of Ir-based catalysts.
- Elucidated the facet-dependent OER mechanism through comprehensive electrochemical characterization and Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations, revealing superior catalytic activity and durability of high-index faceted Pd@Ir nanostructures.
- Contributed to the publication "Unconventional high-index facet of Iridium boosts oxygen evolution reaction: How the Facet Matters" as the third author.
4. Rational Design of Co-Cu/TiO2 Photocatalyst for Efficient CO2 Conversion via MOF-Templated Synthesis
2017.10 - 2019.03
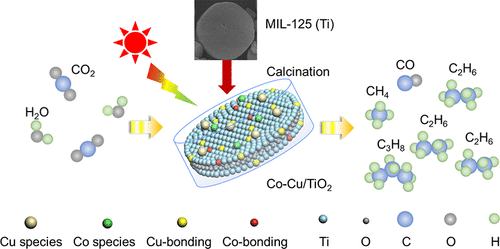
Figure 7: Preparation of Co-Cu/TiO2 using MIL-125(Ti) as a template and its study on CO2 conversion.
- Developed a MOF-templated synthesis strategy using MIL-125(Ti) to fabricate hierarchically porous Co-Cu co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst with precisely controlled surface composition and morphology.
- Elucidated the synergistic effect of Cu and Co dopants on charge carrier dynamics: Cu facilitates efficient photogenerated electron capture and separation, while Co acts as a hole trap and promotes H+ intermediate formation, enhancing C2+ product selectivity.
- Demonstrated superior photocatalytic performance in CO2 reduction with H2O, achieving high selectivity towards value-added C1-C3 products (CO, CH4, C2H6, and C3H8) under simulated solar irradiation.
